The infinite possibilities of microgravity.
Japan's Kibo to realize the hopes of the world.
The International Space Station (ISS) is a giant human facility which has been assembled in space roughly 400 km above the earth. It is a collaborative international project with 15 participating countries/region from all over the world, including the USA, Russia, Europe, and Canada. Kibo is one part of the ISS, developed by Japan. Here, experiments and observations are carried out utilizing the special microgravity environment of space, where gravity is extremely weak compared to the earth.
Kibo received the Good Design Award 2010 G Mark from the Japan Institute of Design Promotion.
 Received the Good Design Gold Award 2010
Received the Good Design Gold Award 2010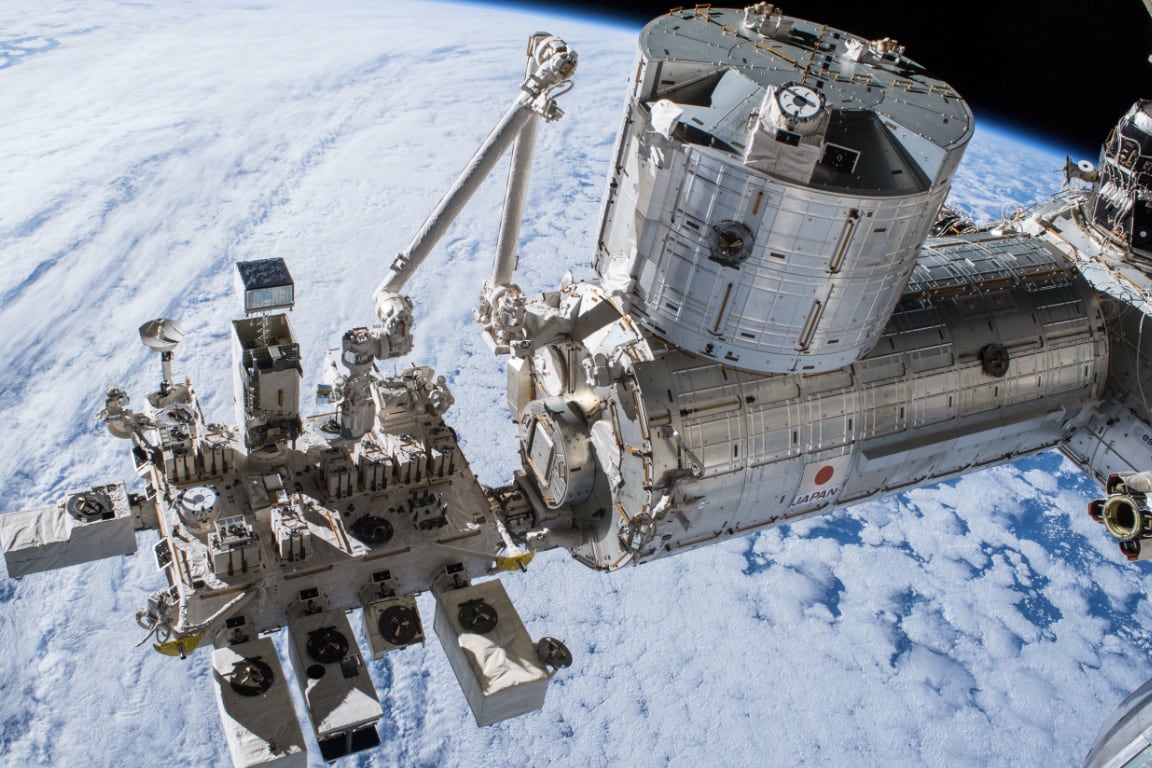
* As of February 9, 2026
The gifts given to us by Kibo.
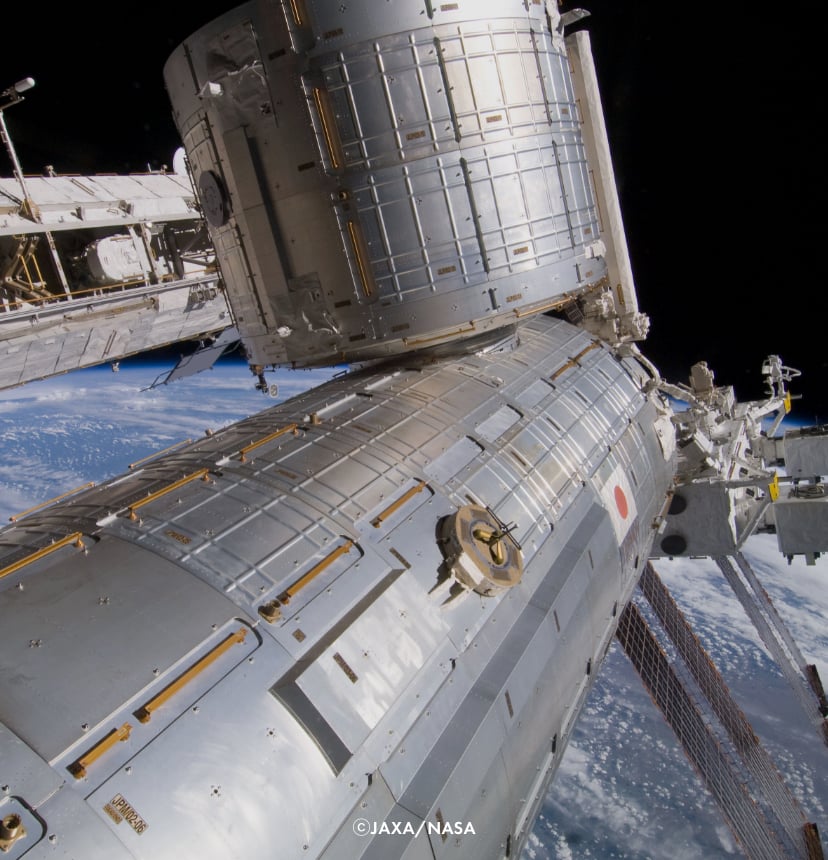
Kibo is the largest module of the ISS.
It is composed of four main elements.
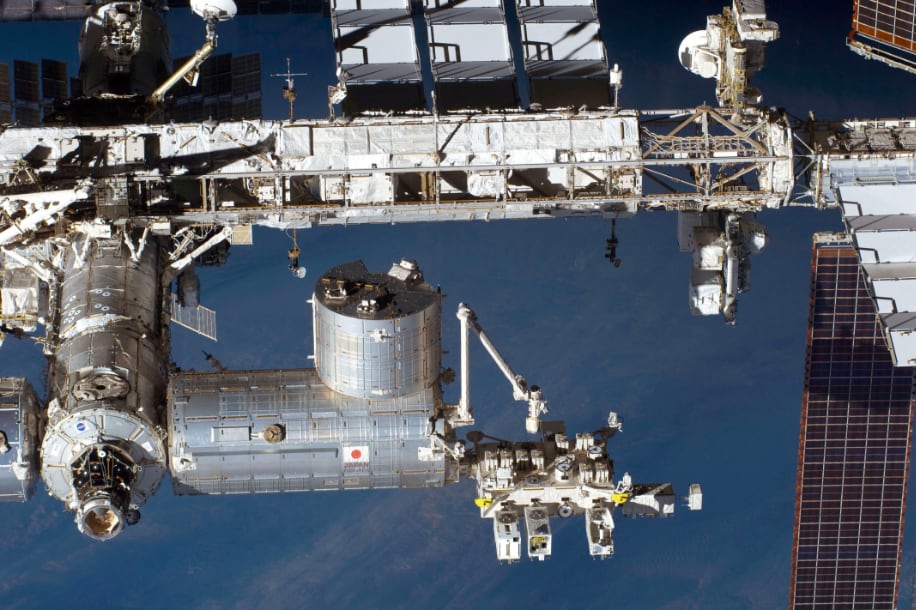

Kibo is an experiment module developed by Japan. It is Japan's first manned facility enabling long-term activities by astronauts, and boasts the largest size of any component of the ISS. Kibo is consisted of two main experiment facilities, internal one called Pressurized Module (PM) and external one called Exposed Facility (EF); storage space called Experiment Logistics Module-Pressurized Section (ELM-ES); and a robotic arm called Japanese Experiment Module Remote Manipulator System (JEMRMS) used for experiments and other tasks.
Space and earth.
Together in spirit, even when far away.
Ground personnels maintain conditions for astronaut activities, and monitor experiment plans and statuses. The Kibo module of the ISS is managed 24 hours a day, 365 days a year, by the Tsukuba Space Center back on earth.
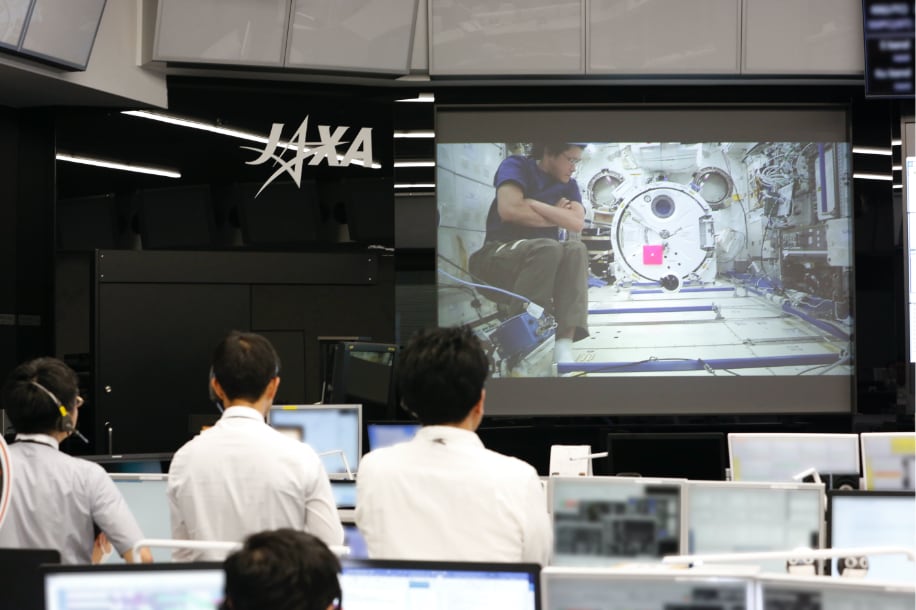

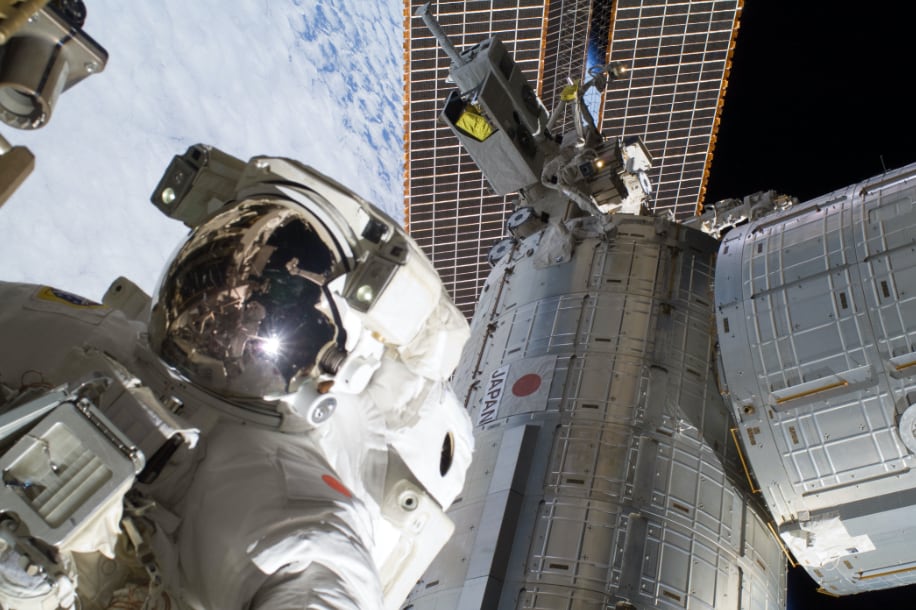
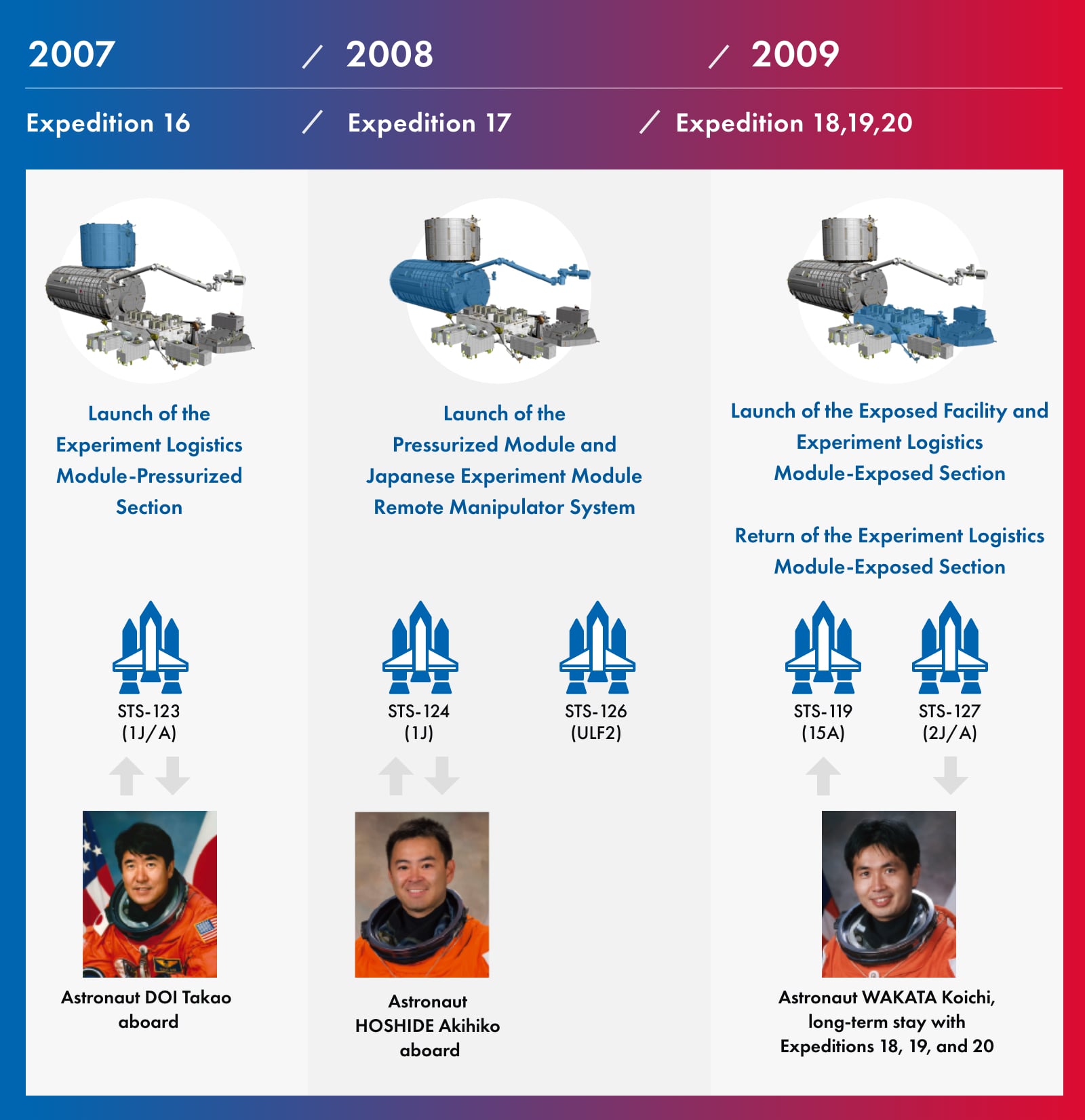
Three Japanese astronauts participated the assembly of Kibo in space

Kibo’s elements were launched by three Space Shuttle missions and assembled with the ISS in space.
The Japanese astronauts DOI Takao, HOSHIDE Akihiko, and WAKATA Koichi participated in the assembly, startup, and testing of Kibo developed by Japan.
Assembly Sequence
Unless specified otherwise, rights to all images belong to ©JAXA















