2021.09.30
- Announcements
AHiS News: Return of spaceflight seeds and ground control experiments
- Kibo Utilization Office for Asia (KUOA)
Introduction
Under the Asian Herb in Space (AHiS) project, basil grown on the International Space Station (ISS) "Kibo" and space flight seeds stored on Kibo were recovered on the ground by SpX-22 on July 10, 2021 (JST). They were then transported from U.S. to Japan, and arrived at JAXA on July 30, 2021.

Mission of AHiS
AHiS consists of two missions:
The objective for Mission 1 is to grow basil on Kibo for about one month. The basil recovered on the ground will be analyzed by researchers to evaluate the effects of the space environment, and students will learn about space biology through the ground control experiment. The experimental equipment was launched by SpX-21 on December 7, 2020, and the initial water supply to the four plant chambers was performed by Astronaut Noguchi on February 16, 2021, to start the experiment.
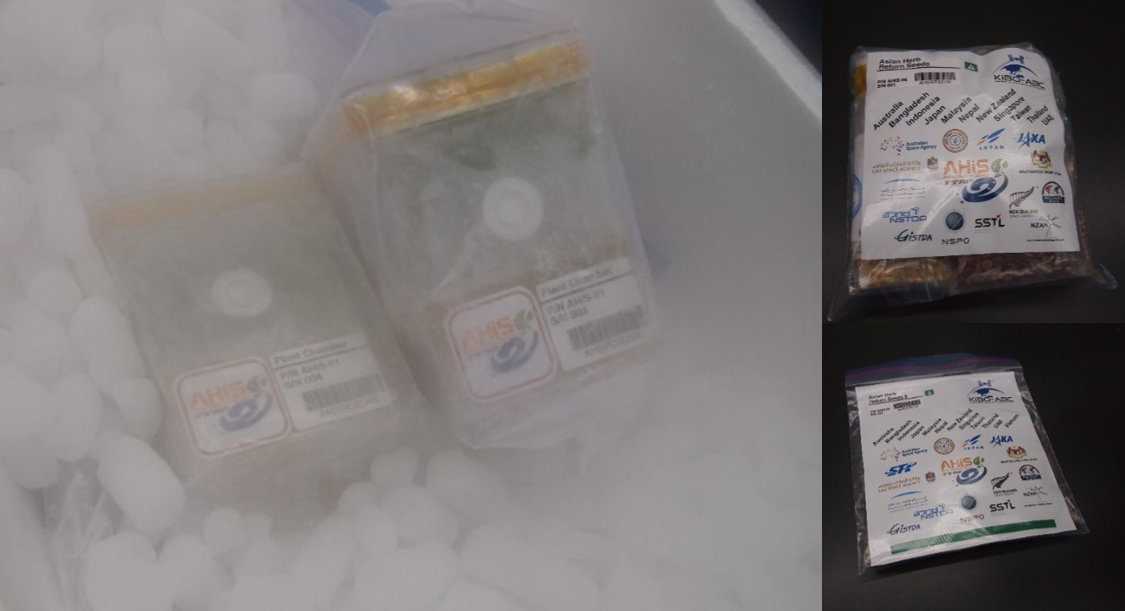
After the completion of the experiment, the plant chambers were frozen and stored in the ISS freezer (MELFI) for recovery on the ground in a frozen state. Figure 1 is a photo of the arrival of the plant chambers at JAXA.
Mission 2 is to provide opportunities for students to study science with the space flight seeds stored and recovered from Kibo. For this mission, 22 herb seeds selected from 11 Kibo-ABC member countries/region were launched in two batches and stored on Kibo for about 7 months or about 1 month respectively.
The space flight seeds that arrived at JAXA had returned to the countries/region that provided them. They are being used already in educational programs in several countries. For specific information from different countries, please see the links below:
Ground control experiment of Mission 1
In the basil cultivation experiment of Mission 1, a ground control experiment was conducted at JAXA's Tsukuba Space Center to compare basil grown in the space environment with basil grown on the ground. In the ground control experiment, we used the same number of seeds as the basil grown in space. We cultivated it for 30 days from August 3 to September 2, simulating the temperature, humidity, carbon dioxide concentration, and light intensity of the basil grown on Kibo.
Detailed analysis is still to be done, but the stems tended to be longer on the basil grown on Kibo than on the ground. Samples from the space experiment and the ground control experiment will be analyzed by researchers in Malaysia and Japan.


Related Links
Unless specified otherwise, rights to all images belong to ©JAXA