- completed
[SMILES]
Superconducting Submillimeter-Wave Limb-Emission Sounder
- Earth and Space Science
ISS Science for Everyone
SCIENCE OBJECTIVES FOR EVERYONE
The Superconducting Submillimeter-Wave Limb-Emission Sounder (SMILES) investigation aims to globally map stratospheric trace gases by means of the most sensitive submillimeter receiver. Although SMILES stopped atmospheric observation due to instrumental failures in April 2010, highly sensitive data obtained for a half year provides accurate global datasets of atmospheric minor constituents related to ozone chemistry. SMILES continues operations for instrumental calibration and cooling of a mechanical cooler, as well as a brush-up of retrieval algorithms for atmospheric constituents.
SCIENCE RESULTS FOR EVERYONE
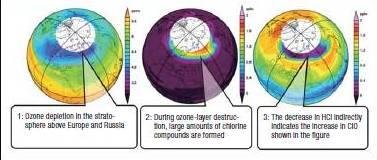
This investigation takes precise measurements of daily constituents in lowest layer of Earth’s atmosphere to help evaluate accuracy of climate models. Data show that daily variation in partial Ice Water Path (pIWP) of ice clouds is strong over land, peaking between late afternoon and early evening, but relatively weak over oceans with peaks at noon and early morning. Further, data show that daily cloud ice mass cycles are complex. Measurement of ozone distribution and short-lived trace atmosphere compounds that can destroy ozone showed ozone loss at different altitudes during Arctic winter. These observations provide a better understanding of the processes controlling stratospheric ozone chemistry and those related to climate change.
Experiment Description
RESEARCH OVERVIEW
- The main scientific target of the SMILES mission is to evaluate quantitatively the recovery and stability of the stratospheric ozone layer. There are still considerable uncertainties in factors affecting ozone levels. There is a need for a detailed understanding of ozone chemistry based on a high sensitive observation.
- SMILES has a high potential to observe atmospheric minor constituents which contribute the ozone depletion in the middle atmosphere.
- SMILES provides accurate global datasets of ozone-depletion gas concentrations and gives important insights into the ozone trend, especially chlorine and bromine compounds related to ozone chemistry.
DESCRIPTION
SMILES (Superconducting Submillimeter-Wave Limb-Emission Sounder) is a sensitive submillimeter-wave sounder. The objective of SMILES is to monitor global distributions of the stratshperic trace gases which contribute ozone depletion. SMILES is the first to use a superconductive low-noise receiver with a mechanical 4-K refrigerator in space to realize a high sensitive observation.
Media Gallery
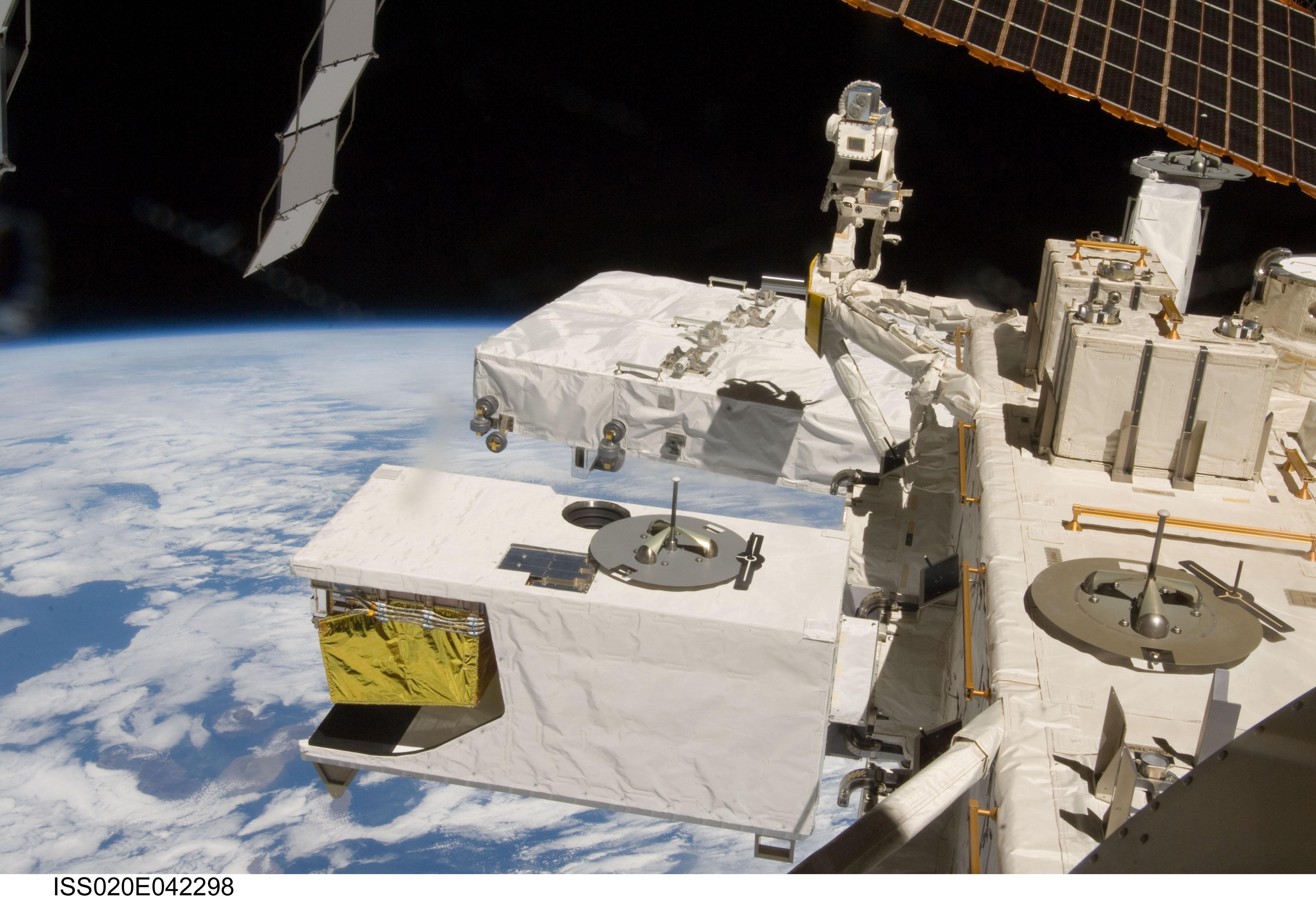

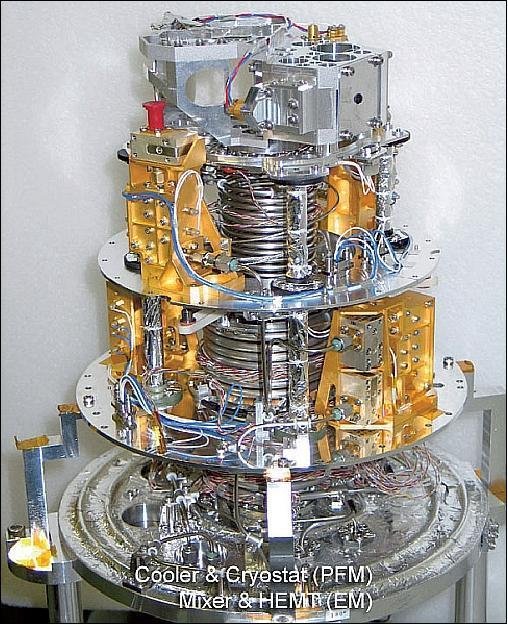
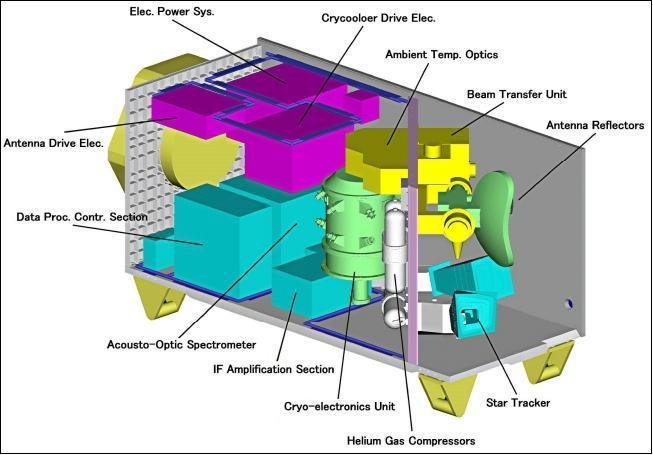
Applications
SPACE APPLICATIONS
The technologies of the cryogenic system used in SMILES may be applied to future spacecraft development.
EARTH APPLICATIONS
The high-sensitivity observations of SMILES improve scientific understanding of processes controlling the stratospheric ozone chemistry and those related to climate change.
Publications
Operations
OPERATIONAL REQUIREMENTS AND PROTOCOLS
SMILES requires cooling operation and instrumental calibration operation. For the cooling operation, low-rate downlink is used. The operation is scheduled four times in 2011, each takes a few weeks to complete. After 2011, a weeklong simplified cooling operation is conducted at annual intervals. For the instrumental calibration operation, both low- and medium-rate downlink are used.
For the cooling operation, two mechanical cryocoolers are operated. Operation procedures aim to achieve a cryogenic temperature of about 4 Kelvin. For the instrumental calibration operation, subsystems related to a signal chain are powered on. The internal calibration signals are generated to investigate the response of the subsystems.
PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR(S)
JAXA/ NICT
Unless specified otherwise, rights to all images belong to ©JAXA



