Unique functions, providing
opportunities to realize frequent,
easy, and varied space experiments
The experiments to be operated on Kibo’s Exposed Facility (EF) will be integrated into the standard EF payload whose size is 0.8m x 1.0m x 1.85m with a weight less than 500kg. The EF can accommodate up to 10 JEM EF payloads. The EF will supply electrical power, coolant fluid, and communications to those payloads.
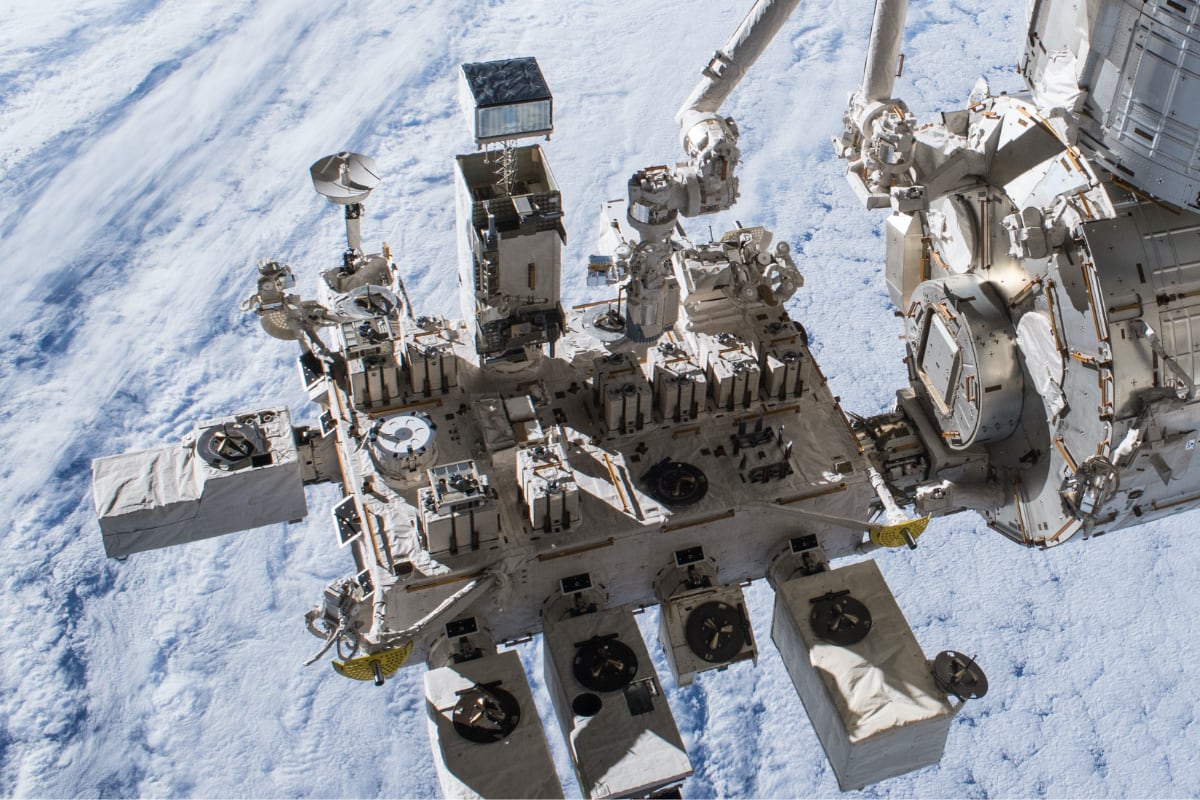
Experimental equipment on Kibo's Exposed Facility
Experimental equipment that has been developed and installed
Installed payloads in the past
Other experimental equipment and assistive devices
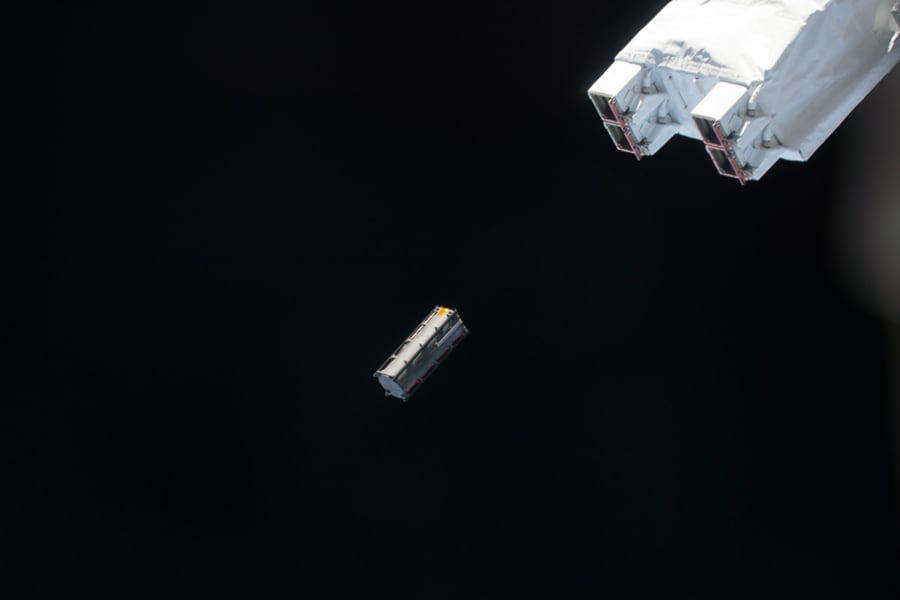
JEM Small Satellite Orbital Deployer (J-SSOD)
Kibo's designated airlock and robotic arm functions are used to carry and release miniaturized satellites from the interior to space. The assistive equipment used in this process is the JEM Small Satellite Orbital Deployer (J-SSOD).
The J-SSOD is a mechanism for launching CubeSat standard miniaturized satellites from Kibo's airlock and putting them into orbit. It consists of the Multi-Purpose Experiment Platform (MPEP), Satellite Install Case, Separation Mechanism, and other equipment.

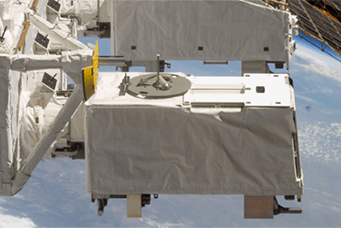
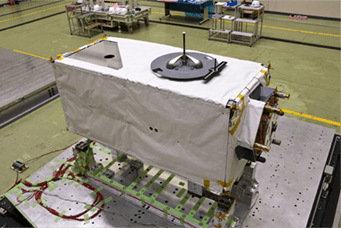
IVA-replaceable Small Exposed Experiment Platform (i-SEEP)
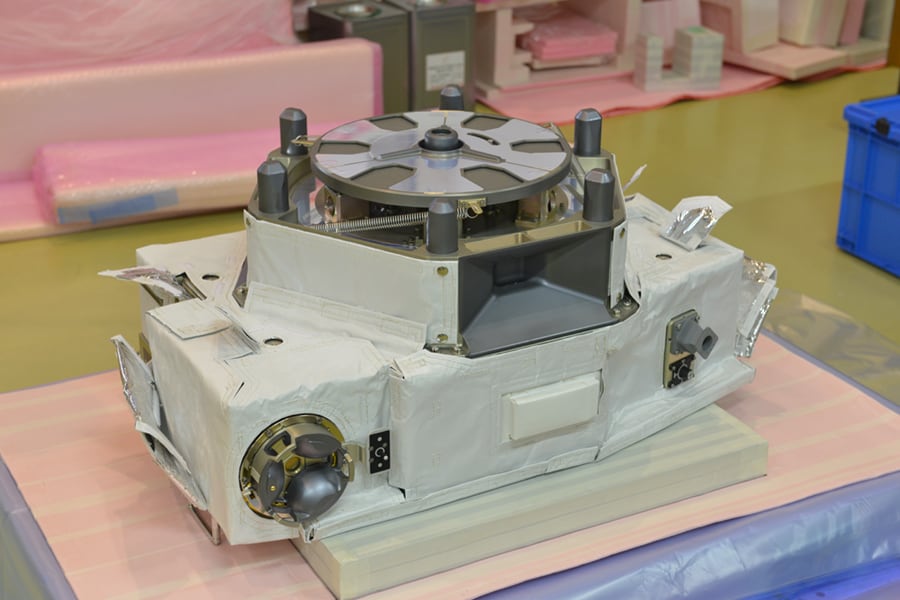

The i-SEEP provides the resources, such as power and communications, for multiple pieces of equipment to be installed. Only mission equipment needs to be developed, making it easier to perform technical demonstration tests, earth observations, and space observations.
As with the J-SSOD, Kibo’s characteristic airlock and robotic arm are used to load mission equipment sent up to the ISS onto the i-SEEP at Kibo. Then, the equipment is transferred to the exterior via the airlock, and installed by the robotic arm at a designated location on Kibo's Exposed Facility. The onboard devices are provided with power, communications (such as commands and telemetry), and other resources during the experiment. The obtained mission data and, if necessary, post-experiment samples and devices are sent back to earth from the ISS, where they are returned to the user.
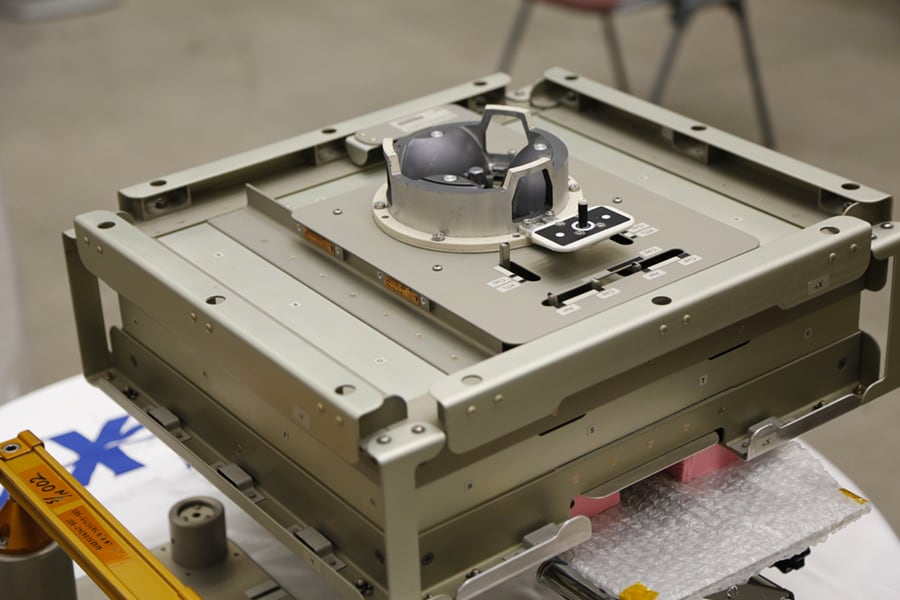
Exposed Experiment Handrail Attachment Mechanism (ExHAM)
The ExHAM is a mechanism that allows small experiment samples to be installed to the exterior of Kibo for purposes such as material exposure experiments using an exposed environment in space. As with the J-SSOD, Kibo’s characteristic airlock and robotic arm are used to load the experiment samples onto the ExHAM at Kibo. The samples are then sent out through the airlock, and are attached to the handrail outside Kibo using the robotic arm.
The ExHAM can hold up to 20 experiment samples of 10 cm2 each in size, which are exposed to the space environment for an arbitrary period of time, and then sent back to earth.
Unless specified otherwise, rights to all images belong to ©JAXA